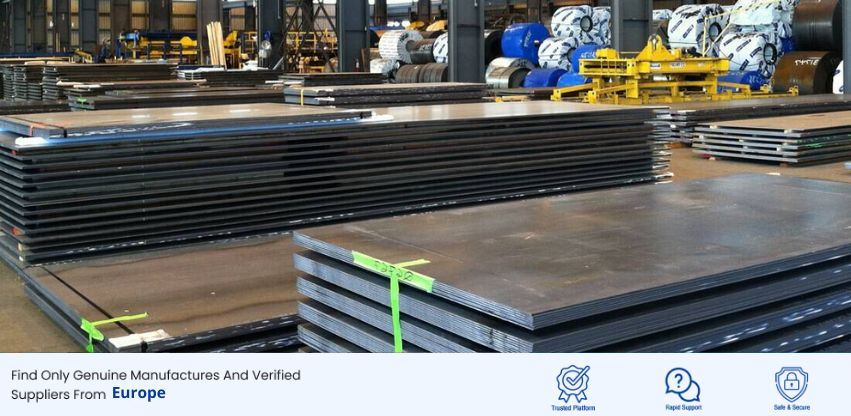
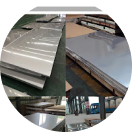
Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate Manufacturers, Suppliers & Exporters in Europe - PipingProjects.eu
PipingProjects.eu is one of the leading Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate Manufacturer in Europe. We are renowned for our comprehensive range of high-quality plates designed to withstand extreme conditions. As a trusted Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate Supplier in Europe, we prioritize precision engineering, rigorous quality control measures, and adherence to international standards to ensure the reliability and longevity of our products. With an unwavering commitment to innovation and customer satisfaction, PipingProjects.eu continues to set the standard for excellence in the Quenched and Tempered Steel Plate manufacturing industry.
What is Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate?
Quenched and Tempered Steel Plate is a specialized type of steel plate that undergoes a specific heat treatment process to enhance its mechanical properties. The steel plate is first heated to a high temperature and then rapidly cooled, or quenched, in water, oil, or other quenching mediums. This rapid cooling causes the steel to harden, increasing its strength and toughness.
After quenching, the steel plate is tempered by reheating it to a lower temperature. Tempering helps to reduce the internal stresses created during quenching and improves the steel's flexibility and toughness while maintaining a high level of strength. The precise temperature and duration of the tempering process are carefully controlled to achieve the desired balance of strength and toughness for the specific application.
Top leading Manufacturing Companies
What are the grades of Quenched And Tempered Steel?
Quenched and Tempered Steel Grades, characterized by a carbon content of 0.25% to 0.6%, are available in alloyed and non-alloyed forms and are renowned for their strength enhancement through heat treatment. Notably, processes involving high-temperature heating followed by rapid cooling and tempering contribute to increased hardness and improved toughness of steel and iron-based alloys.
ASTM A514 and ASTM A710 are prominent examples of such grades, prized for their high strength and durability. Widely used across industries, these grades find applications in critical structural components and machinery parts subjected to heavy loads and abrasive conditions, ensuring reliability and longevity in diverse industrial settings.

Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate
Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate - Specifications
- Product : Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate
- Thickness : 4mm to 160mm
- Width : 1525mm to 3100mm
- Length : 4000mm to 9000mm
- Standards : JIS, AISI, ASME, ASTM, AMS, GB, DIN, EN, GOST
- Delivery : Quenched and Tempered

Trusted
Supplier

Genuine
Product
Easy
purchase
Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate Specification Chart
Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate Specification & Grades
| Product |
Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate |
| Standard |
ASTM A514 and A514M-13 |
| Thickness |
4mm to 160mm |
| Length |
4000mm to 9000mm |
| Width : |
1525mm to 3100mm |
| Delivery Condition: |
Quenched and Tempered |
| Finish |
Rolled |
| Grade |
| Quenched & Tempered Steel
|
Grade 400, 80 and 500, WELTEN 140 KSI, 780E, 130 KSI, A514, S890Q, A710, TMCP 100 KSI, RQT 701, S690QL, S690QL1, S890QL1, S690Q, S890QL, Weldox 700, S960QL |
What are the differences between Quenched & Tempered Steel and Normalized Steel?
- Quenched and tempered steel and normalized steel are both heat treatment processes used to enhance the properties of steel, but they differ in their methods and resulting characteristics. Quenching and tempering involve heating the steel to a high temperature, followed by rapid cooling (quenching) and then tempering to improve toughness and ductility. This process results in steel with high strength and hardness.
- It is suitable for applications requiring robust materials that can withstand heavy loads, such as structural components in machinery, construction, and mining equipment. In contrast, normalized steel undergoes a different heat treatment process where the steel is heated to a specific temperature and then cooled in still air. This process primarily aims to refine the grain structure and relieve internal stresses, resulting in steel with improved machinability, uniformity, and dimensional stability.
- Quenched and tempered steel typically exhibits higher strength, hardness, and wear resistance than normalized steel. It is often preferred for applications requiring superior mechanical performance and resistance to abrasion and impact. On the other hand, normalized steel offers improved machinability and weldability due to its refined grain structure, making it suitable for components that require extensive machining or welding operations. The choice between quenched and tempered steel and normalized steel depends on the specific requirements of the application, including factors such as strength, machinability, and weldability, allowing for tailored solutions across various industrial sectors.
Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate Chemical Composition
Explore our accurate Quenched & Tempered Steel Chemical Composition Chart, essesntial for diverse applications, with insights from a leading Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate Supplier in Europe, ensuring adherence to quality standards and performance reliability.
Chemical Composition of Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate
|
A514 Gr B |
A514 Gr A |
A514 Gr E |
A514 Gr C |
A514 Gr Q |
A514 Gr H |
A514 Gr S |
A514 Gr M |
A514 Gr F |
A514 Gr K |
A514 Gr J |
A514 Gr R |
A514 Gr P |
A514 Gr T |
| C |
0.012-0.021 |
0.015-0.021 |
0.012-0.020 |
0.010-0.020 |
0.014-0.021 |
0.012-0.021 |
0.011-0.021 |
0.012-0.021 |
0.010-0.020 |
0.010-0.020 |
0.012-0.021 |
0.015-0.020 |
0.012-0.021 |
0.008-0.014 |
| M |
0.070-1.000 |
0.080-1.010 |
0.040-0.070 |
1.010-1.050 |
0.095-1.030 |
0.095-1.030 |
1.010-1.050 |
0.045-0.070 |
0.060-1.000 |
1.010-1.050 |
0.045-0.070 |
0.085-1.015 |
0.045-0.070 |
1.020-1.050 |
| P |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
| S |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
0.0035 |
0.0010 |
| Si |
0.020-0.035 |
0.040-0.080 |
0.020-0.040 |
0.015-0.030 |
0.015-0.035 |
0.020-0.035 |
0.015-0.045 |
0.020-0.035 |
0.015-0.035 |
0.015 |
0.020-0.035 |
0.020-0.035 |
0.020-0.035 |
0.040-0.060 |
| Ni |
- |
- |
- |
- |
1.020-1.050 |
0.030-0.070 |
- |
1.020-1.050 |
0.070-1.000 |
- |
- |
0.090-1.010 |
1.020-1.050 |
- |
| Cr |
0.040-0.065 |
0.050-0.080 |
1.040-2.000 |
- |
1.000-1.050 |
0.040-0.065 |
- |
- |
0.040-0.065 |
- |
- |
0.035-0.065 |
0.085-1.020 |
- |
| Mo |
0.015-0.025 |
0.018-0.028 |
0.040-0.060 |
0.015-0.030 |
0.045-0.060 |
0.020-0.030 |
0.010-0.060 |
0.045-0.060 |
0.040-0.060 |
0.045-0.060 |
0.050-0.065 |
0.015-0.025 |
0.045-0.060 |
0.045-0.060 |
| V |
0.003-0.008 |
- |
- |
- |
0.003-0.008 |
0.003-0.008 |
0.006 |
- |
0.003-0.008 |
- |
- |
0.003-0.008 |
- |
0.003-0.008 |
| Ti |
0.001-0.003 |
- |
0.001-0.010 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| Z |
|
0.005-0.015 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| Cu |
- |
- |
0.015-0.050 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.015-0.050 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| B |
0.0001-0.0005 |
0.00025 |
0.0001-0.0005 |
0.0001-0.0005 |
- |
0.0001-0.0005 |
0.0001-0.0005 |
0.0001-0.0005 |
0.0001-0.0005 |
0.0001-0.0005 |
0.0001-0.0005 |
- |
0.0001-0.0005 |
0.0001-0.0005 |
| Nb |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.006 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate Mechanical Properties
Discover the mechanical prowess of Quenched & Tempered Steel Plates, including strength and ductility, provided by a prominent Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate Manufacturer in Europe, ensuring top-tier quality for a range of industrial applications.
Mechanical Properties of Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate
|
Grade
|
A514 Mechanical Property
|
|
Tensile
|
Yield
|
Elongation
|
Thickness
|
|
A514
|
Mpa
|
Min Mpa
|
Min %
|
mm
|
|
760-895
|
690
|
18
|
20
|
|
760-895
|
690
|
18
|
20-65
|
|
690-895
|
620
|
18
|
65-150
|
Properties of Quenched & Tempered Steel Plates
- Quenched and Tempered Steel Plates possess distinctive properties that are highly sought-after in various industrial applications. One of their key attributes is exceptional strength derived from the heat treatment. By subjecting the steel to high temperatures followed by rapid quenching and subsequent tempering, these plates achieve heightened hardness and toughness, rendering them capable of withstanding heavy loads and harsh working environments.
- This combination of strength and toughness is critical in construction, mining, and manufacturing industries, where components are subjected to high stress and abrasion.
- Quenched and Tempered Steel Plates exhibit superior wear resistance, making them ideal for applications involving abrasive materials or environments. Their ability to resist deformation and maintain structural integrity under extreme conditions ensures long-term reliability and performance in critical machinery components, pressure vessels, and structural frameworks.
- Additionally, these plates offer excellent weldability and machinability, facilitating ease of fabrication and assembly in diverse industrial settings. Overall, the exceptional properties of Quenched and Tempered Steel Plates, including strength, toughness, wear resistance, weldability, and machinability, make them indispensable materials for a wide range of applications requiring high-performance structural solutions.
Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate Size Chart
Explore our comprehensive Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate Size Range ensuring optimal performance and longevity. As a well-known Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate Supplier in Europe, we provide detailed information for informed decision-making in various industrial applications.
Size Chart of Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate
| THICKNESS |
GRADE |
LENGTH |
WIDTH |
| 3/16 – 1 1/4 inch |
GRADE B |
UP TO 480 inch |
48" – 120" |
| INQUIRE |
GRADE P |
INQUIRE |
INQUIRE |
| 3/16 – 2 1/2 inch |
GRADE S |
UP TO 480 inch |
48" – 120" |
| 3/16 – 2 inch |
GRADE H |
UP TO 480 inch |
48" – 120" |
| 3/16– 8 inch |
GRADE Q |
UP TO 480 inch |
48" – 120" |
| 3/16 – 2 1/2 inch |
GRADE F |
UP TO 480 inch |
48" – 120" |
| INQUIRE |
GRADE A |
INQUIRE |
INQUIRE |
| 3/16 – 6 inch |
GRADE E |
UP TO 480 inch |
48" – 120" |
Applications of Quenched & Tempered Steel Plates in Europe?
- Quenched and Tempered Steel Plates find wide-ranging applications across industries requiring high-strength, durable materials capable of withstanding harsh conditions. These plates are commonly used to construct heavy machinery, such as bulldozers, excavators, and cranes, where strength and resistance to abrasion and impact are paramount.
- Additionally, Quenched and Tempered Steel Plates are extensively used in manufacturing pressure vessels and boilers, providing the necessary strength to withstand high temperatures and pressures encountered in industrial settings. In the automotive industry, these plates are employed to fabricate critical components like chassis frames and suspension systems, ensuring structural integrity and safety under demanding operating conditions.
- Quenched and Tempered Steel Plates play a vital role in producing mining equipment, including haul truck bodies, buckets, and drill rigs, where they offer exceptional wear resistance and durability in abrasive environments. In the construction sector, these plates are utilized to fabricate structural elements such as bridges, building frameworks, and offshore platforms, providing reliable performance and long-term stability.
- Quenched and Tempered Steel Plates are also employed in the defence industry for manufacturing armoured vehicles, ensuring superior protection against ballistic threats while maintaining manoeuvrability and operational efficiency. Overall, the versatility and high-performance characteristics of Quenched and Tempered Steel Plates make them indispensable in various industrial applications where strength, durability, and reliability are paramount.
Weight Chart of Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate
As a trusted Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate Manufacturer in Europe, we provide comprehensive weights information to facilitate accurate decision-making in various applications.
Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate Weight Chart
| Thickness (inches) |
Density (lbs/in³8.72 g/cm³) |
DSS Plate Weight per Unit Area |
|
|
lbs/in² |
kg/m² |
| 3/16 |
0.315 |
0.06000 |
42.184176 |
| 1/4 |
0.315 |
0.08 |
56.245568 |
| 3/8 |
0.315 |
0.121 |
85.0714216 |
| 1/2 |
0.315 |
0.161 |
113.1942056 |
| 5/8 |
0.315 |
0.196 |
137.8016416 |
| 3/4 |
0.315 |
0.235 |
165.221356 |
| 7/8 |
0.315 |
0.274 |
192.6410704 |
| 1 |
0.315 |
0.313 |
220.0607848 |
| 1 1/4 |
0.315 |
0.391 |
274.9002136 |
| 1 1/2 |
0.315 |
0.47 |
330.442712 |
| 1 3/4 |
0.315 |
0.549 |
385.9852104 |
| 2 |
0.315 |
0.627 |
440.8246392 |
| 2 1/4 |
0.315 |
0.705 |
495.664068 |
| 2 1/2 |
0.315 |
0.784 |
551.2065664 |
| 2 3/4 |
0.315 |
0.862 |
606.0459952 |
| 3 |
0.315 |
0.941 |
661.5884936 |
Advantages of using Quenched & Tempered Steel Plates
- High Strength:
Enhanced mechanical properties, including high tensile strength and hardness, make these plates suitable for applications requiring robust structural integrity.
- Cost-Effectiveness:
While initial costs may be higher, the extended service life and reduced maintenance expenses contribute to long-term cost savings.
- Improved Toughness:
The tempering process enhances toughness and flexibility, ensuring the plates can withstand impact and dynamic loads without fracturing.
- Reliability:
The controlled heat treatment process ensures uniformity and consistency in material properties, enhancing reliability and performance.
- Weldability:
Despite their high strength, these plates maintain good weldability, allowing for easy fabrication and assembly in various applications.
- Compliance with Standards:
Quenched & Tempered Steel Plates adhere to stringent industry standards and specifications, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and safety standards.
Various Types of Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate We Supply
PipingProjects.eu is a leading Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate Supplier in Europe. We supply different types of Quenched & Tempered Steel Plates to meet diverse industrial needs with superior quality and precision.
Are Quenched & Tempered steel plates suitable for high-temperature applications?
- Quenched and Tempered Steel Plates are generally not recommended for high-temperature applications where sustained exposure to elevated temperatures is expected. While these plates exhibit excellent mechanical properties, including high strength and toughness, their performance can be compromised under prolonged exposure to high temperatures.
- The tempering process during heat treatment helps improve the toughness and flexibility of the steel. Still, it may need to adequately address the effects of high temperatures on the material's microstructure. Prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures can lead to a phenomenon known as temper embrittlement, where the steel may lose its toughness and become susceptible to cracking or failure.
- Other types of steel with specialized compositions and heat treatment processes, such as heat-resistant or high-temperature steels, are more suitable for high-temperature applications. These steels are designed to maintain their mechanical properties and structural integrity at elevated temperatures, ensuring reliable performance in demanding thermal environments.
- Quenched and Tempered Steel Plates are excellent for strength, toughness, and wear resistance applications. However, they should be used within their specified temperature limits to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Manufacturing Process of Quenched & Tempered Steel Plates
Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate is produced in seven steps. It manufactures a wide range of shapes, goods, and parts, ranging from Quenched & Tempered Steel Plate and Coil.
- Step 1 : Raw Material Selection
To begin the process of creating alloy steel, raw materials such as iron ore and other elements including nickel, chromium, and molybdenum are carefully selected. The choice of alloying elements depends on the specific properties that the alloy steel is intended to possess.
- Step 2 : Smelting and Melting
Once the raw materials have been selected, they are smelted in a furnace to create a molten metal alloy. The composition of the alloy is closely monitored and controlled to achieve the desired grade of alloy steel.
- Step 3 : Forming
After the molten alloy steel has been produced, it is cast into different shapes and forms, depending on its intended use. The most common shapes include slabs, billets, blooms, or ingots.
- Step 4 : Primary & Secondary Steelmaking
The subsequent step is primary steelmaking, which can be accomplished through different methods such as the Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF) or the Electric Arc Furnace (EAF). At this stage, impurities like carbon are eliminated to achieve the desired chemical composition.
- Step 5 : Casting
The molten alloy steel is then cast into semi-finished forms, which can take the shape of plates, sheets, bars, or other forms. Continuous casting or ingot casting methods are usually employed for this purpose.
- Step 6 : Hot Rolling
In the case of products like Quenched & Tempered Steel Plates, the semi-finished castings are hot-rolled to achieve the desired thickness and shape. During this process, the thickness of the castings is reduced while improving their mechanical properties.
- Step 7 : Cold Rolling and Annealing
In the case of specific alloy steel products such as thin sheets and coils, cold rolling is employed to further reduce the thickness and enhance surface finish. To relieve stresses and enhance corrosion resistance, annealing is frequently performed.